# 继续看Render
上一篇讲到调用render函数渲染vnode,这里从render函数继续:
// packages/react-dom/src/client/ReactDOMRoot.js
function ReactDOMRoot(internalRoot: FiberRoot) {
this._internalRoot = internalRoot;
}
ReactDOMRoot.prototype.render = function(
children: ReactNodeList,
): void {
const root = this._internalRoot;
if (root === null) {
throw new Error('Cannot update an unmounted root.');
}
...
updateContainer(children, root, null, null);
};
...
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
这行代码updateContainer(children, root, null, null);其中root便是传进去的去的参数document.getElementById("root")然后创建的vnode,children便是上面的
可以看到这个函数的children是ReactNodeList类型,可为什么可以渲染
# 了解源码的方法
react源码项目尝试了启动不起来,去网上找了个不错的react源码调试环境项目https://github.com/neroneroffy/react-source-code-debug.git,略读了一下react源码解析的文章。在之后的源码分析中,需要注意一下几点:
给IDE配置好项目的路径别名。
源码是变化的,分析的方向首先需要确定源码解决的问题是什么,然后朝着解决问题的思路去了解。至于细节技巧看懂就看,看不懂略过也没关系,看个人兴趣。
问题应该是自己想了解的,或曾经遇到的。啥都没有那就先不用看,毕竟分析源码只是了解或借鉴。只有当你自己输出或解决你的问题时,才是真理。
必须借助方法调用图、模块结构图。然后webstorm的diagram生成工具可以作为辅助。
# Render
好了,开始用上面的git仓库来构建我的react源码调试环境吧!
新建src/components/RenderProcess文件夹,新建一下index.js文件。
// src/components/RenderProcess/index.js
import React from 'react';
const Game = () => {
return <div>a good start</div>
}
export default Game
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
然后再src/App.js里引入该组件。ok,正常运行!可以开始调试了。在上一篇的那段代码打上断点:
// src/react/v18/react-dom/src/client/ReactDOMRoot.js
ReactDOMHydrationRoot.prototype.render = ReactDOMRoot.prototype.render = function(
children: ReactNodeList,
): void {
const root = this._internalRoot;
if (root === null) {
throw new Error('Cannot update an unmounted root.');
}
...
updateContainer(children, root, null, null);
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
在浏览器调试可以看到:
root参数的类型即为FiberRootNode,其containerInfo是其对应的dom节点。
children这个参数类型是ReactNodeList,其值有点奇怪的是一个对象类型,有type,props,ref,key,这些属性。这个type是入口App函数类型(同时可以看看函数调用栈)。
然后看看updateContainer函数(旧版的):
// src/react/v18/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberReconciler.old.js
export function updateContainer(
element: ReactNodeList,
container: OpaqueRoot,
parentComponent: ?React$Component<any, any>,
callback: ?Function,
): Lane {
...
const current = container.current;
const eventTime = requestEventTime();
const lane = requestUpdateLane(current);
if (enableSchedulingProfiler) {
markRenderScheduled(lane);
}
const context = getContextForSubtree(parentComponent);
if (container.context === null) {
container.context = context;
} else {
container.pendingContext = context;
}
...
const update = createUpdate(eventTime, lane);
// Caution: React DevTools currently depends on this property
// being called "element".
update.payload = {element};
callback = callback === undefined ? null : callback;
if (callback !== null) {
if (__DEV__) {
if (typeof callback !== 'function') {
console.error(
'render(...): Expected the last optional `callback` argument to be a ' +
'function. Instead received: %s.',
callback,
);
}
}
update.callback = callback;
}
enqueueUpdate(current, update, lane);
const root = scheduleUpdateOnFiber(current, lane, eventTime);
if (root !== null) {
entangleTransitions(root, current, lane);
}
return lane;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
这里突然返回一个lane变量(意为通道,道路的意思),从这句代码update.payload = {element};可以看到,把element(react nodelist类型)当做载荷放到了update那里去。那update是什么来的呢?是通过const update = createUpdate(eventTime, lane);创建的,lane又是啥?
const current = container.current;
const lane = requestUpdateLane(current);
2
去打个断点看看把,这变量不知哪里窜出来的。呃呃呃,看了下源码一层套一层,打断点了在文件夹跳来跳去也晕了,得画一下方法调用图,模块结构图才行,不然难搞。
# 程序入口调用关系图
来看下基础的方法调用关系图吧:
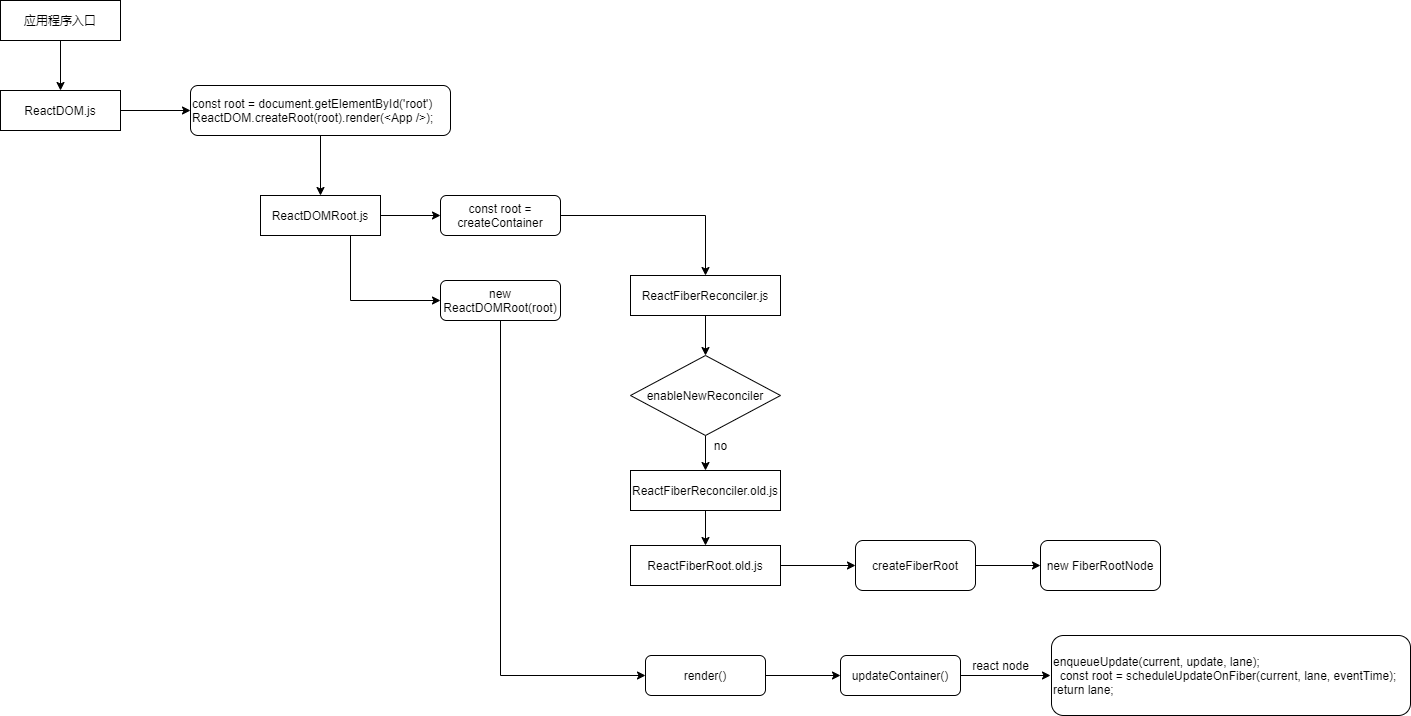
可以看到上面的图有两处需要关注的地方,一点是创建了root fiber对象、二点是ReactDomRoot对象调用render对象,这个render包含enqueueUpdate将Update插入队列、scheduleUpdateOnFiber未知。
然后接下来了解一下调用render方法相关的事情。
# Lane
看看render方法返回的lane变量是啥,虽然程序入口拿到lane后啥也没做* — *。可以看到通过requestUpdateLane方法创建了lane。
// src/react/v18/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberWorkLoop.old.js
export function requestUpdateLane(fiber: Fiber): Lane {
debugger
// Special cases
const mode = fiber.mode;
if ((mode & ConcurrentMode) === NoMode) {
return (SyncLane: Lane);
} else if (
!deferRenderPhaseUpdateToNextBatch &&
(executionContext & RenderContext) !== NoContext &&
workInProgressRootRenderLanes !== NoLanes
) {
return pickArbitraryLane(workInProgressRootRenderLanes);
}
const isTransition = requestCurrentTransition() !== NoTransition;
if (isTransition) {
if (__DEV__ && ReactCurrentBatchConfig.transition !== null) {
const transition = ReactCurrentBatchConfig.transition;
if (!transition._updatedFibers) {
transition._updatedFibers = new Set();
}
transition._updatedFibers.add(fiber);
}
if (currentEventTransitionLane === NoLane) {
// All transitions within the same event are assigned the same lane.
currentEventTransitionLane = claimNextTransitionLane();
}
return currentEventTransitionLane;
}
const updateLane: Lane = (getCurrentUpdatePriority(): any);
if (updateLane !== NoLane) {
return updateLane;
}
const eventLane: Lane = (getCurrentEventPriority(): any);
return eventLane;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
看了代码不理解lane,百度了一下react 16版本之后加入了优先级模式,然后从WorlLoop名字可以看出是新的代码运行机制:工作循环(不要用js事件循环那套机制了,react优先级从底层RIC中断了原本的事件循环机制)
React有三套优先级机制:
- React事件优先级
- Lane优先级
- Scheduler优先级
上面代码requestUpdateLane是获取工作优先级。首先会判断是否为ConcurrentMode并发模式,不是的话使用就使用同步模式。然后再依次判断其他的优先级。lane直译为车道,是一种优先级模式,采用二进制来表示(可能类似硬件中断的优先级方式)。
这里再了解一下其中的getCurrentEventPriority:
// src/react/v18/react-dom/src/client/ReactDOMHostConfig.js
export function getCurrentEventPriority(): * {
const currentEvent = window.event;
if (currentEvent === undefined) {
return DefaultEventPriority;
}
return getEventPriority(currentEvent.type);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// src/react/v18/react-dom/src/events/ReactDOMEventListener.js
switch (domEventName) {
// Used by SimpleEventPlugin:
case 'cancel':
case 'click':
case 'close':
case 'contextmenu':
case 'copy':
case 'cut':
case 'auxclick':
case 'dblclick':
case 'dragend':
case 'dragstart':
case 'drop':
case 'focusin':
case 'focusout':
case 'input':
case 'invalid':
case 'keydown':
case 'keypress':
case 'keyup':
case 'mousedown':
case 'mouseup':
case 'paste':
case 'pause':
case 'play':
case 'pointercancel':
case 'pointerdown':
case 'pointerup':
case 'ratechange':
case 'reset':
case 'resize':
case 'seeked':
case 'submit':
case 'touchcancel':
case 'touchend':
case 'touchstart':
case 'volumechange':
// Used by polyfills:
// eslint-disable-next-line no-fallthrough
case 'change':
case 'selectionchange':
case 'textInput':
case 'compositionstart':
case 'compositionend':
case 'compositionupdate':
// Only enableCreateEventHandleAPI:
// eslint-disable-next-line no-fallthrough
case 'beforeblur':
case 'afterblur':
// Not used by React but could be by user code:
// eslint-disable-next-line no-fallthrough
case 'beforeinput':
case 'blur':
case 'fullscreenchange':
case 'focus':
case 'hashchange':
case 'popstate':
case 'select':
case 'selectstart':
return DiscreteEventPriority;
case 'drag':
case 'dragenter':
case 'dragexit':
case 'dragleave':
case 'dragover':
case 'mousemove':
case 'mouseout':
case 'mouseover':
case 'pointermove':
case 'pointerout':
case 'pointerover':
case 'scroll':
case 'toggle':
case 'touchmove':
case 'wheel':
// Not used by React but could be by user code:
// eslint-disable-next-line no-fallthrough
case 'mouseenter':
case 'mouseleave':
case 'pointerenter':
case 'pointerleave':
return ContinuousEventPriority;
case 'message': {
// We might be in the Scheduler callback.
// Eventually this mechanism will be replaced by a check
// of the current priority on the native scheduler.
const schedulerPriority = getCurrentSchedulerPriorityLevel();
switch (schedulerPriority) {
case ImmediateSchedulerPriority:
return DiscreteEventPriority;
case UserBlockingSchedulerPriority:
return ContinuousEventPriority;
case NormalSchedulerPriority:
case LowSchedulerPriority:
// TODO: Handle LowSchedulerPriority, somehow. Maybe the same lane as hydration.
return DefaultEventPriority;
case IdleSchedulerPriority:
return IdleEventPriority;
default:
return DefaultEventPriority;
}
}
default:
return DefaultEventPriority;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
示例代码是返回DefaultEventPriority。
# createUpdate
而const update = createUpdate(eventTime, lane);其实是直接创建一个对象,把lane作为其中一个属性:
// src/react/v18/react-reconciler/src/ReactUpdateQueue.old.js
export function createUpdate(eventTime: number, lane: Lane): Update<*> {
const update: Update<*> = {
eventTime,
lane,
tag: UpdateState,
payload: null,
callback: null,
next: null,
};
return update;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
然后把要更新的组件添加上去:update.payload = {element};
然后看enqueueUpdate(current, update, lane);
// src/react/v18/react-reconciler/src/ReactUpdateQueue.old.js
export function enqueueUpdate<State>(
fiber: Fiber,
update: Update<State>,
lane: Lane,
) {
const updateQueue = fiber.updateQueue;
if (updateQueue === null) {
// Only occurs if the fiber has been unmounted.
return;
}
const sharedQueue: SharedQueue<State> = (updateQueue: any).shared;
if (isInterleavedUpdate(fiber, lane)) {
const interleaved = sharedQueue.interleaved;
if (interleaved === null) {
// This is the first update. Create a circular list.
update.next = update;
// At the end of the current render, this queue's interleaved updates will
// be transferred to the pending queue.
pushInterleavedQueue(sharedQueue);
} else {
update.next = interleaved.next;
interleaved.next = update;
}
sharedQueue.interleaved = update;
} else {
const pending = sharedQueue.pending;
if (pending === null) {
// This is the first update. Create a circular list.
update.next = update;
} else {
update.next = pending.next;
pending.next = update;
}
sharedQueue.pending = update;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
可以看到是在fiber上的队列。
# scheduleUpdateOnFiber
来看看这个函数:
// src/react/v18/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberWorkLoop.old.js
export function scheduleUpdateOnFiber(
fiber: Fiber,
lane: Lane,
eventTime: number,
): FiberRoot | null {
checkForNestedUpdates();
const root = markUpdateLaneFromFiberToRoot(fiber, lane);
if (root === null) {
return null;
}
// Mark that the root has a pending update.
markRootUpdated(root, lane, eventTime);
if (
(executionContext & RenderContext) !== NoLanes &&
root === workInProgressRoot
) {
// This update was dispatched during the render phase. This is a mistake
// if the update originates from user space (with the exception of local
// hook updates, which are handled differently and don't reach this
// function), but there are some internal React features that use this as
// an implementation detail, like selective hydration.
warnAboutRenderPhaseUpdatesInDEV(fiber);
// Track lanes that were updated during the render phase
workInProgressRootRenderPhaseUpdatedLanes = mergeLanes(
workInProgressRootRenderPhaseUpdatedLanes,
lane,
);
} else {
// This is a normal update, scheduled from outside the render phase. For
// example, during an input event.
if (enableUpdaterTracking) {
if (isDevToolsPresent) {
addFiberToLanesMap(root, fiber, lane);
}
}
warnIfUpdatesNotWrappedWithActDEV(fiber);
if (enableProfilerTimer && enableProfilerNestedUpdateScheduledHook) {
if (
(executionContext & CommitContext) !== NoContext &&
root === rootCommittingMutationOrLayoutEffects
) {
if (fiber.mode & ProfileMode) {
let current = fiber;
while (current !== null) {
if (current.tag === Profiler) {
const {id, onNestedUpdateScheduled} = current.memoizedProps;
if (typeof onNestedUpdateScheduled === 'function') {
onNestedUpdateScheduled(id);
}
}
current = current.return;
}
}
}
}
if (enableTransitionTracing) {
const transition = ReactCurrentBatchConfig.transition;
if (transition !== null) {
if (transition.startTime === -1) {
transition.startTime = now();
}
addTransitionToLanesMap(root, transition, lane);
}
}
if (root === workInProgressRoot) {
// TODO: Consolidate with `isInterleavedUpdate` check
// Received an update to a tree that's in the middle of rendering. Mark
// that there was an interleaved update work on this root. Unless the
// `deferRenderPhaseUpdateToNextBatch` flag is off and this is a render
// phase update. In that case, we don't treat render phase updates as if
// they were interleaved, for backwards compat reasons.
if (
deferRenderPhaseUpdateToNextBatch ||
(executionContext & RenderContext) === NoContext
) {
workInProgressRootInterleavedUpdatedLanes = mergeLanes(
workInProgressRootInterleavedUpdatedLanes,
lane,
);
}
if (workInProgressRootExitStatus === RootSuspendedWithDelay) {
// The root already suspended with a delay, which means this render
// definitely won't finish. Since we have a new update, let's mark it as
// suspended now, right before marking the incoming update. This has the
// effect of interrupting the current render and switching to the update.
// TODO: Make sure this doesn't override pings that happen while we've
// already started rendering.
markRootSuspended(root, workInProgressRootRenderLanes);
}
}
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, eventTime);
if (
lane === SyncLane &&
executionContext === NoContext &&
(fiber.mode & ConcurrentMode) === NoMode &&
// Treat `act` as if it's inside `batchedUpdates`, even in legacy mode.
!(__DEV__ && ReactCurrentActQueue.isBatchingLegacy)
) {
// Flush the synchronous work now, unless we're already working or inside
// a batch. This is intentionally inside scheduleUpdateOnFiber instead of
// scheduleCallbackForFiber to preserve the ability to schedule a callback
// without immediately flushing it. We only do this for user-initiated
// updates, to preserve historical behavior of legacy mode.
resetRenderTimer();
flushSyncCallbacksOnlyInLegacyMode();
}
}
return root;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
这函数看不出头绪,勉强看到ensureRootIsScheduled(root, eventTime);这个可以了解一下。
// Use this function to schedule a task for a root. There's only one task per
// root; if a task was already scheduled, we'll check to make sure the priority
// of the existing task is the same as the priority of the next level that the
// root has work on. This function is called on every update, and right before
// exiting a task.
function ensureRootIsScheduled(root: FiberRoot, currentTime: number) {
const existingCallbackNode = root.callbackNode;
// Check if any lanes are being starved by other work. If so, mark them as
// expired so we know to work on those next.
markStarvedLanesAsExpired(root, currentTime);
// Determine the next lanes to work on, and their priority.
const nextLanes = getNextLanes(
root,
root === workInProgressRoot ? workInProgressRootRenderLanes : NoLanes,
);
if (nextLanes === NoLanes) {
// Special case: There's nothing to work on.
if (existingCallbackNode !== null) {
cancelCallback(existingCallbackNode);
}
root.callbackNode = null;
root.callbackPriority = NoLane;
return;
}
// We use the highest priority lane to represent the priority of the callback.
const newCallbackPriority = getHighestPriorityLane(nextLanes);
// Check if there's an existing task. We may be able to reuse it.
const existingCallbackPriority = root.callbackPriority;
if (
existingCallbackPriority === newCallbackPriority &&
// Special case related to `act`. If the currently scheduled task is a
// Scheduler task, rather than an `act` task, cancel it and re-scheduled
// on the `act` queue.
!(
__DEV__ &&
ReactCurrentActQueue.current !== null &&
existingCallbackNode !== fakeActCallbackNode
)
) {
if (__DEV__) {
// If we're going to re-use an existing task, it needs to exist.
// Assume that discrete update microtasks are non-cancellable and null.
// TODO: Temporary until we confirm this warning is not fired.
if (
existingCallbackNode == null &&
existingCallbackPriority !== SyncLane
) {
console.error(
'Expected scheduled callback to exist. This error is likely caused by a bug in React. Please file an issue.',
);
}
}
// The priority hasn't changed. We can reuse the existing task. Exit.
return;
}
if (existingCallbackNode != null) {
// Cancel the existing callback. We'll schedule a new one below.
cancelCallback(existingCallbackNode);
}
// Schedule a new callback.
let newCallbackNode;
if (newCallbackPriority === SyncLane) {
// Special case: Sync React callbacks are scheduled on a special
// internal queue
if (root.tag === LegacyRoot) {
if (__DEV__ && ReactCurrentActQueue.isBatchingLegacy !== null) {
ReactCurrentActQueue.didScheduleLegacyUpdate = true;
}
scheduleLegacySyncCallback(performSyncWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root));
} else {
scheduleSyncCallback(performSyncWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root));
}
if (supportsMicrotasks) {
// Flush the queue in a microtask.
if (__DEV__ && ReactCurrentActQueue.current !== null) {
// Inside `act`, use our internal `act` queue so that these get flushed
// at the end of the current scope even when using the sync version
// of `act`.
ReactCurrentActQueue.current.push(flushSyncCallbacks);
} else {
scheduleMicrotask(() => {
// In Safari, appending an iframe forces microtasks to run.
// https://github.com/facebook/react/issues/22459
// We don't support running callbacks in the middle of render
// or commit so we need to check against that.
if (
(executionContext & (RenderContext | CommitContext)) ===
NoContext
) {
// Note that this would still prematurely flush the callbacks
// if this happens outside render or commit phase (e.g. in an event).
flushSyncCallbacks();
}
});
}
} else {
// Flush the queue in an Immediate task.
scheduleCallback(ImmediateSchedulerPriority, flushSyncCallbacks);
}
newCallbackNode = null;
} else {
let schedulerPriorityLevel;
switch (lanesToEventPriority(nextLanes)) {
case DiscreteEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = ImmediateSchedulerPriority;
break;
case ContinuousEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = UserBlockingSchedulerPriority;
break;
case DefaultEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = NormalSchedulerPriority;
break;
case IdleEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = IdleSchedulerPriority;
break;
default:
schedulerPriorityLevel = NormalSchedulerPriority;
break;
}
newCallbackNode = scheduleCallback(
schedulerPriorityLevel,
performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root),
);
}
root.callbackPriority = newCallbackPriority;
root.callbackNode = newCallbackNode;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
发现里面的schedule优先级了。里面还有其他函数都不懂,先进行到这里,后面继续了解直到看到渲染就ok了。
这分析源码是一个逆向工程,我只是想了解而已,但还是比较费时费力的。还是找个教程作为辅助比较好一些,看看这个https://react.iamkasong.com/。